

LCP Equations
Definitions:
- χ is the Euler-Poincare characteristic
- A* is the area of the surface in the unit cell with the lattice parameter equals to unity
- Γis the topology index,
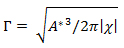
- γ is the lipid shape factor
- Vis the volume per lipid molecule
- A(ξ)is the area at distance ξ from IPMS
- lis the lipid length
- ais the LCP lattice parameter
- Φis the volume fraction of lipids in LCP
- rwis the water channel radius
Table 1. Geometrical Properties of IPMS
| Spacegroup | Ia3d, Q230 | Pn3m, Q224 | Im3m, Q229 |
| IPMS type | G, gyroid | D, diamond | P, primitive |
| gerrymander’s walk | devil’s delight | plumber’s nightmare | |
| Γ | 0.767 | 0.750 | 0.717 |
| χ | -8 | -2 | -4 |
| A* | 3.091 | 1.919 | 2.345 |
Spacing Ratio for X-ray Reflections (International Tables for Crystallography):
Ia3d: √ 6:√ 8:√ 14:√ 16:√ 20:√ 22:√ 24:√ 26
Pn3m: √ 2:√ 3:√ 4:√ 6:√ 8:√ 9:√ 10:√ 11:√ 12:√ 14:√ 16:√ 17
Im3m: √ 2:√ 4:√ 6:√ 8:√ 10:√ 12:√ 14:√ 16:√ 18:√ 20:√ 22:√ 24:√ 26
IPMS approximations (Rummel et al., 1998).
| Ia3d: | Sin(x) Cos(y) + Sin(y) Cos(z) + Sin(z) Cos(x) = 0, where –π < x < 3 π, -π< y <3 π, -π< z < π | (1) |
| Pn3m: | Sin(x) Sin(y) Sin(z) + Sin(x) Cos(y) Cos(z) + Cos(x) Sin(y)Sin(z) + Cos(x) Cos(y) Sin(z) = 0, where 0 < x <2.5 π, 0 < y < 2.5 π, -0.5 π < z < 1.5 π |
(2) |
| Im3m: | Cos(x) + Cos(y) + Cos(z) = 0, where –π< x < 3 π, -π < y < 3 π, -π < z < π | (3) |
| Volume fraction of lipids (Qiu and Caffrey, 1998): | |
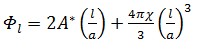 |
(4) |
This equation can be used to numerically calculate the lipid length l. |
|
| Surface area at distance ξ from IPMS (Anderson et al., 1988): | |
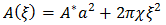 |
(5) |
| Radius of water channels (from Eq.5): | |
 |
(6) |
| Lipid shape factor (Qiu and Caffrey, 2000): | |
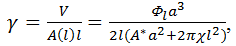 |
(7) |
REFERENCES:
Anderson, D.M., Gruner, S.M., and S. Leibler (1988) Geometrical aspects of the frustration in the cubic phases of lyotropic liquid crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 5364-5368.
Qiu, H, and M. Caffrey (1998) Lyotropic and thermotropic phase behavior of hydrated monoacylglycerols: structure characterization of monovaccenin. J. Phys. Chem. B 102: 4819-4829.
Qiu, H., and M. Caffrey (2000) The phase diagram of monoolein/water system: metastability and equilibrium aspects. Biomaterials 21: 223-234.
Rummel, G., Hardmeyer, A., Widmer, C., Chiu, M.L., Nollert, P., Locher, K.P., Pedruzzi, I., Landau, E.M., and J.P. Rosenbusch. (1998) Lipidic cubic phases: new matrices for the three-dimensional crystallization of membrane proteins. J. Struct. Biol. 121: 82-91.
CONTACT US: USC | Cherezov Lab | cherezov@usc.edu